Recognizing and Managing Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) in Seniors
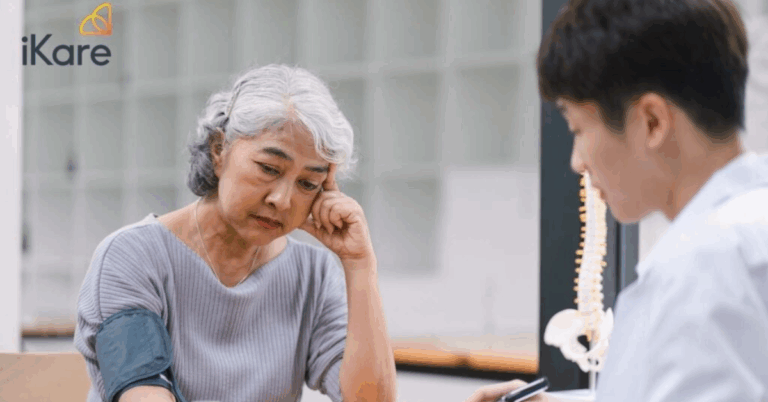
betbazar 247 login, playexch in login, gold365 id login: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) can be a challenging condition to manage, especially for seniors. COPD is a progressive lung disease that makes it difficult to breathe. It includes conditions such as emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Symptoms include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
As individuals age, their lung function naturally declines, which can exacerbate COPD symptoms. It’s essential for seniors with COPD to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their condition effectively. Here are some tips for recognizing and managing COPD in seniors:
1. Know the Symptoms: Understanding the symptoms of COPD can help seniors recognize when they may be experiencing a flare-up of their condition. Symptoms can vary from person to person but commonly include increased breathlessness, frequent coughing, chest tightness, and increased mucus production. If seniors experience any new or worsening symptoms, they should contact their healthcare provider.
2. Stay Active: Regular physical activity can help improve lung function and overall quality of life for seniors with COPD. Encourage seniors to engage in activities that they enjoy, such as walking, swimming, or tai chi. It’s essential to start slowly and gradually increase activity levels to avoid exacerbating symptoms.
3. Follow a Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help seniors maintain a healthy weight and reduce inflammation in the body. Seniors with COPD should also limit their intake of processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats, as these can worsen symptoms.
4. Quit Smoking: Smoking is the leading cause of COPD, and quitting smoking is the most effective way to slow the progression of the disease. Seniors who smoke should speak to their healthcare provider about smoking cessation programs and resources to help them quit.
5. Take Medications as Prescribed: Seniors with COPD may be prescribed medications to help manage their symptoms, such as bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and oxygen therapy. It’s essential for seniors to take their medications as prescribed by their healthcare provider and report any side effects or concerns promptly.
6. Monitor Symptoms: Seniors with COPD should keep track of their symptoms and any changes in their condition. This information can help healthcare providers adjust treatment plans as needed. Seniors can use a symptom tracker or journal to monitor their symptoms and share this information with their healthcare provider.
7. Avoid Respiratory Irritants: Seniors with COPD should avoid exposure to respiratory irritants that can worsen their symptoms, such as air pollution, dust, strong odors, and secondhand smoke. Seniors should also stay indoors on days with high pollution levels or poor air quality.
8. Stay Up-to-Date on Vaccinations: Seniors with COPD are at higher risk for respiratory infections, such as pneumonia and the flu. It’s essential for seniors to stay current on vaccinations, including the annual flu shot and pneumonia vaccine, to reduce their risk of complications from these infections.
9. Practice Breathing Techniques: Breathing techniques, such as pursed lip breathing and diaphragmatic breathing, can help seniors with COPD improve their lung function and manage their symptoms. Seniors can work with a respiratory therapist to learn these techniques and practice them regularly.
10. Seek Support: Managing COPD can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Seniors with COPD should seek support from family, friends, and support groups to help them cope with their condition. Counseling or therapy may also be beneficial for seniors struggling with anxiety or depression related to their COPD.
In conclusion, recognizing and managing COPD in seniors requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medication management, and regular monitoring of symptoms. By following these tips and working closely with their healthcare providers, seniors with COPD can improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of their condition.
FAQs:
Q: Can COPD be cured?
A: COPD is a chronic, progressive disease that cannot be cured. However, treatment can help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
Q: What is the difference between COPD and asthma?
A: COPD and asthma are both respiratory conditions that can cause breathing difficulties. However, asthma is typically diagnosed at a younger age and is often triggered by allergies, while COPD is more common in older adults and is usually caused by smoking.
Q: Is oxygen therapy necessary for all seniors with COPD?
A: Oxygen therapy may be prescribed for some seniors with COPD to help improve oxygen levels in the blood. Not all seniors with COPD will require oxygen therapy, but it may be necessary for those with severe or advanced disease.